In the world of fluid and gas control systems, motorized ball valves have become a staple due to their versatility, reliability, and ease of use. Known for their ability to regulate the flow of liquids and gases in a variety of applications, motorized ball valves, or electric ball valves, are highly favored in both industrial and residential settings. By using an electric actuator to rotate a ball with a bore through a pipe, these valves offer precise control over the flow of a medium, providing a simple, efficient solution for automated systems.
This article explores the mechanics, applications, and troubleshooting of motorized ball valves, as well as their advantages and common issues that users may encounter.
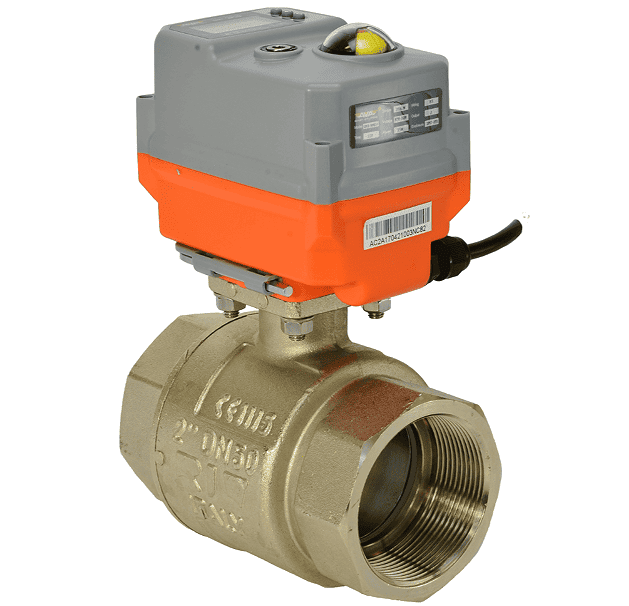
A motorized ball valve, often referred to as an electric ball valve, is a device used to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. The fundamental working mechanism involves a ball with a hole, or bore, that rotates within the valve body. The rotation of the ball is controlled by an electric actuator, which connects to the valve stem. This actuator rotates the ball a quarter turn, thus opening or closing the valve to control the flow.
The two main components of a motorized ball valve are:
Electric Actuator (Servo Motor): This is the electric motor that powers the valve’s rotation, either opening or closing the valve as needed.
Ball Valve: The ball valve contains a spherical ball with a hole, and it controls the flow of fluid by rotating within the valve body.
The electric actuator and the ball valve are typically mounted together and standardized with a flange that adheres to ISO 5211, allowing for easy replacement or interchangeability of the valve and actuator without needing to change the flange size.
Motorized ball valves are popular in many industries due to their simple design, reliability, longevity, and ease of automation. They are widely used in water control systems, heating units, and various industrial processes, making them essential in both residential and commercial applications.
Motorized ball valves serve a wide range of applications, from managing water in residential settings to regulating chemicals in industrial facilities. Below are some of the most common uses for motorized ball valves:
Motorized ball valves are extensively used in heating systems, such as boilers and radiators, to control the flow of hot water. By regulating the flow, these valves ensure that heat is evenly distributed across the entire building, improving energy efficiency and enhancing user comfort. In larger commercial buildings or multi-floor residential complexes, motorized ball valves allow for automated regulation of temperature and heat distribution.
In agricultural applications, motorized ball valves play a critical role in irrigation systems. These valves help regulate water flow across different sections of the land, ensuring an efficient distribution of water. By controlling water usage in this way, motorized ball valves contribute significantly to water conservation, especially in areas experiencing water scarcity.
In industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage production, motorized ball valves are essential for controlling the flow of various fluids or gases. The precise control they provide ensures the safety, efficiency, and consistency of the processes. For example, in chemical manufacturing, these valves can control the flow of corrosive chemicals, ensuring that safety protocols are met while optimizing production.
In many modern home appliances like washing machines and dishwashers, motorized ball valves are used to control the flow of water into the machine. By regulating water intake, these valves ensure that the correct amount of water is used for each cycle, preventing waste and improving the appliance’s efficiency.
In water treatment plants, motorized ball valves are used to control the flow of water and treatment chemicals. By maintaining precise control over water and chemical distribution, these valves help ensure that the treatment process is both safe and effective, contributing to the delivery of clean, potable water.
Despite their reliability, motorized ball valves can experience issues over time. Here are some common problems and solutions to help you keep your valve functioning properly:
Troubleshooting and Fixes:
Power Supply: Ensure that the power source is operational. Check the wiring and confirm that the controller is sending the appropriate signal to the actuator.
Actuator Failure: If the actuator is malfunctioning, the valve may not open or close properly. Inspect the actuator for any signs of damage, and listen for unusual sounds during operation. If the actuator is defective, it will likely need to be replaced.
Obstruction: Foreign objects or debris inside the valve can block its movement. Remove any obstructions within the valve or the actuator to ensure smooth operation.
Troubleshooting and Fixes:
Low Voltage: A low voltage supply can cause sluggish or erratic valve behavior. Measure the voltage at the valve terminals and compare it with the manufacturer’s specifications. If the voltage is too low, inspect the power source and wiring for issues.
Friction: Insufficient lubrication may cause the valve to move slowly. Check the valve components for adequate lubrication, and apply the recommended type of lubricant as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Electrical Interference: Nearby equipment may disrupt the electrical components of the actuator. If electrical interference is suspected, move the valve away from the source of interference or install shielding around the valve.
Valve Wear: Over time, parts of the valve can experience wear and tear. Inspect moving components for signs of damage or friction. Replace any worn-out parts to restore normal valve function.
Troubleshooting and Fixes:
Worn Seals: Valve seals wear out over time, leading to leaks. If you notice leakage, check the seals for signs of damage or wear. Replace any damaged seals to stop the leak.
Loose Connections: Leaks can also occur if the connections between the actuator, valve body, and piping are loose. Ensure that all connections are tightened securely to prevent leaks.
High Pressure: If the pressure in the system exceeds the valve’s rated capacity, leaks can occur. Verify that the valve is rated for the pressure in your system. If necessary, install a pressure regulator or use a valve rated for higher pressure.
Improper Installation: Misalignment during installation can lead to seal failure and leaks. Ensure that all components are aligned properly and securely installed to avoid future issues.
Motorized ball valves are a critical component in many modern systems, offering efficient and reliable flow control for a wide range of applications. From industrial processes to home appliances, these valves play an essential role in managing fluids and gases. By understanding how they work, their applications, and how to troubleshoot common issues, users can ensure that their motorized ball valves continue to operate smoothly for years to come. Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting will help avoid costly repairs and replacements, keeping systems running efficiently.
For industries and homes that require automation and remote control of fluid flow, motorized ball valves provide a simple yet effective solution to meet these needs. Their durability, versatility, and ease of use make them a cornerstone in fluid management systems across the globe.