In fluid handling systems, preventing backflow is crucial for maintaining system integrity, preventing contamination, and ensuring operational efficiency. One of the most reliable and efficient solutions for this task is the dual plate check valve, also referred to as a dual disc check valve, non-return valve, or retainerless check valve. These valves are designed to allow flow in a single direction while automatically preventing reverse flow, safeguarding pipelines and equipment from potential damage caused by backpressure or fluid reversal.
Dual plate check valves are widely used across various industries for their compact design, lightweight construction, minimal pressure drop, and high durability. This article provides an in-depth overview of dual plate check valves, discussing their design, working principles, benefits, types, and applications in modern industrial systems.
A dual plate check valve is a mechanical, self-acting valve designed to block the reverse flow of fluids. It features two semicircular plates (or discs) that pivot on a central hinge pin, allowing fluid to flow in one direction and automatically closing when the flow ceases or reverses. The spring-assisted plates respond quickly to pressure changes, making these valves ideal for systems where fast closure is critical to prevent water hammer or pressure surges.
These valves are integral to systems handling gases, liquids, or steam, and are particularly favored in applications requiring minimal maintenance and low-pressure drop. Their retainerless design further enhances reliability, especially in applications involving corrosive or hazardous media.
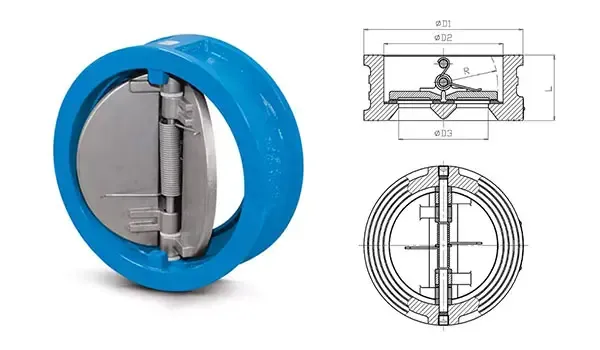
Dual plate check valves are built to meet a variety of industrial needs, with the following notable features:
Compact and Lightweight: Their slim profile and wafer-style body reduce the weight and installation space required compared to swing check valves.
Low Pressure Drop: The streamlined flow path reduces resistance, minimizing energy loss across the valve.
Non-Slam Action: Spring-assisted closure ensures the valve shuts smoothly without the slamming effect, protecting piping systems from water hammer.
Versatile Installation: Suitable for both horizontal and vertical piping orientations.
Tight Shut-Off: Designed to prevent external leakage and ensure a leak-proof seal.
Corrosion Resistance: Available in a variety of materials including stainless steel, carbon steel, and exotic alloys, enabling compatibility with aggressive fluids.
Long Service Life: Engineered for durability and reduced maintenance in demanding conditions.
The functionality of a dual plate check valve relies on the dynamic behavior of its internal plates and spring mechanism. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
Forward Flow: As fluid pressure increases in the direction of intended flow, it pushes against the two plates. The plates pivot around the hinge pin, opening inward and allowing fluid to pass through the valve with minimal resistance.
Flow Cessation or Reversal: When the flow decreases or begins to reverse, the torsion spring and backpressure act simultaneously on the plates. This causes the plates to close quickly and tightly against the valve seat.
Backflow Prevention: With the plates closed, reverse flow is effectively blocked, protecting upstream equipment and processes from contamination or damage.
This mechanism ensures high responsiveness and a tight shut-off, even under low-flow conditions.
There are several variants of dual plate check valves, each tailored to specific operational needs. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the right valve for your system.
These valves are designed to handle specific applications where reducing the flow rate is necessary without completely obstructing it. Common in water systems, they ensure that water flows only in one direction while minimizing flow disruptions.
Benefits:
Simple design
Cost-effective
Prevents reverse flow in moderate-pressure systems
Applications:
Domestic water supply lines
Low-pressure industrial fluid systems
A non-slam check valve incorporates a spring-loaded mechanism to ensure the plates close before the flow reversal occurs. This "soft close" operation prevents the sudden stop of backflow that could cause a pressure shock or water hammer.
Benefits:
Eliminates water hammer
Prolongs piping and valve life
Quick response to flow changes
Applications:
HVAC systems
Pump discharge lines
Oil and gas transport systems
The wafer-style dual plate check valve is one of the most common configurations due to its space-saving design. It fits snugly between two flanges and requires no additional support, making it ideal for tight installations.
Benefits:
Compact and easy to install
Lightweight
Lower material cost
Applications:
Chemical processing
Food and beverage industries
Steam systems
Pharmaceutical systems
Retainerless check valves eliminate the use of through-bolts (retainers), which traditionally penetrate the valve body to secure the internal components. This design reduces the risk of leakage, especially in critical service applications with hazardous fluids.
Benefits:
No external leakage path
Enhanced safety for toxic or high-pressure services
Ideal for aggressive or corrosive environments
Applications:
Offshore oil platforms
Chemical plants
High-pressure gas lines
Compared to conventional swing check valves and lift check valves, dual plate check valves offer a range of performance and operational advantages:
Energy Efficiency: The low-pressure drop minimizes energy consumption by reducing pumping requirements.
Fast Response Time: Spring-loaded plates close faster, providing better protection in dynamic systems.
Reduced Maintenance: Fewer moving parts and robust construction lead to less wear and tear.
Versatility: Can be used in clean or dirty services, horizontal or vertical pipelines, and across a wide pressure and temperature range.
Noise Reduction: Non-slam design helps lower noise levels in high-speed flow systems.
Dual plate check valves are versatile and used in a wide range of industrial and commercial settings, including:
Petroleum Refining: To prevent backflow in fuel transport and refining operations.
Power Generation: In cooling water systems, condensate return, and boiler feed lines.
Water Treatment Plants: Ensures unidirectional flow in clean and wastewater lines.
Offshore Oil Rigs: Used for their compact size and ability to withstand harsh marine environments.
HVAC Systems: Installed in chilled water and heating systems to maintain flow direction.
Chemical Processing: Handles corrosive fluids while preventing cross-contamination.
Dual plate check valves are manufactured using various materials to meet specific fluid compatibility and pressure requirements. Common materials include:
Body Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel (304/316), ductile iron, bronze, duplex steel, and exotic alloys like Hastelloy and Monel.
Disc Materials: Stainless steel, CF8M, or coated steel for enhanced wear resistance.
Seat Materials: Metal-to-metal or soft seats such as EPDM, PTFE, or Viton for tight shut-off.
These valves are typically designed and tested in accordance with international standards such as:
API 594: Standard for check valve design
API 6D: Specification for pipeline valves
ASME B16.34: Pressure-temperature ratings
DIN/EN Standards: For European market applications
For optimal performance and extended service life, consider the following best practices:
Installation Orientation: Ensure the valve is installed with proper flow direction indicated on the body. Suitable for both horizontal and vertical lines.
Regular Inspection: Periodically check for signs of wear, especially on the hinge pin, spring, and seats.
Cleaning: Remove debris buildup to avoid disc obstruction and improper sealing.
Spare Parts: Keep critical spare parts like springs and seals on hand for quick replacements.
The dual plate check valve represents a reliable, efficient, and compact solution for preventing reverse flow in modern fluid systems. With its streamlined design, non-slam operation, and adaptability across diverse applications, it has become an industry standard in sectors ranging from power generation and petrochemicals to HVAC and water treatment.
Understanding the design, function, and proper selection of dual plate check valves can lead to more reliable system performance, reduced downtime, and lower operational costs. Whether you're an engineer, procurement manager, or system designer, investing in high-quality dual plate check valves ensures your pipeline infrastructure operates smoothly and safely.
Previous: What is a Gate Valve Used For?